Introduction to Wind Power Turbines
Wind Power-Wind Turbine
A wind turbine, also known as a wind power converter, is a device that converts the kinetic power of wind into electrical power. It is essentially a reverse electric fan. Instead of using electricity to generate wind, wind turbines use wind power to generate electricity.
When the wind is strong enough, the blades of the rotating wind turbine can be blown. The wind turbine blades are connected to the generator by means of a low-speed shaft, a gearbox and a high-speed shaft.


Wind energy -Historical footprint
As early as 3000 BC, in Egypt, people used wind power for the first time in the form of sailboats. The sail captures the power of the wind to make the boat travel on the water.
The earliest windmills that used to grind grain appeared in Babylon in 2000 BC or Ancient Persia in 200 BC. These early equipment consisted of one or more vertically installed wooden beams, and there is a knife grinder at the bottom of the wooden beams, which attached to a rotating shaft that turns with the wind. The concept of using wind power to grind grain quickly spread throughout the Middle East and was widely used before the first windmill appeared in Europe. From the 11th century AD, European Crusaders brought this concept home, and the Dutch windmill that we are familiar with was born.
Wind power - The component of wind power generation
1. Tower
One of the most notable components of a wind turbine is its tall tower. What people usually see is a tower wind turbine with a height of more than 200 feet and it does not consider the height of the blade. The height of the wind turbine blades can easily increase the total height of the wind turbine by 100 feet on the basis of the tower.
There is a ladder on the tower for maintenance personnel to enter the top of the turbine, and a high-voltage cable is installed and laid on the tower to transmit the electricity generated by the generator on the top of the turbine to its base.
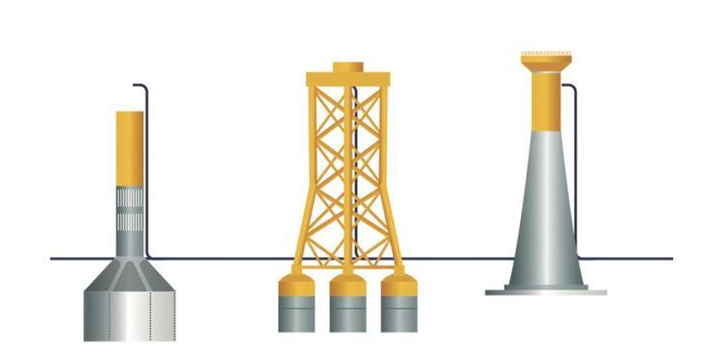
2. Engine compartment
On the top of the tower, people will enter the engine compartment, which is a streamlined shell containing the internal components of the wind turbine. The appearance of engine compartment looks like a square box and is located at the top of the tower.
The engine compartment provides protection for important internal components of the wind turbine. These components include generators, gearboxes, and low-speed and high-speed shafts.
3. Paddle
Paddle act as wind barriers. When the wind forces the blades to move, paddle will transferred some power to the rotor.
And the wind turbine shaft is connected to the center of the rotor. When the rotor rotates, the shaft also rotates. In this way, the rotor transfers its mechanical and rotational power to the shaft, and then the shaft enters the generator at the other end.

It uses the characteristics of electromagnetic induction to generate voltage (the difference in charge). Voltage is essentially an electric pressure, which is the force that moves electricity or current from one point to another. So generating voltage is actually generating current. A simple generator is composed of magnets and conductors. The conductor is usually a coiled wire. Inside the generator, the shaft is connected with permanent magnets surrounding the coil. In electromagnetic induction, if you have a conductor surrounded by magnets, one part of which rotates relative to the other, it will induce a voltage in the conductor. When the rotor rotates the shaft, the shaft rotates the magnet assembly, it will generate a voltage across the wire of the coil. This voltage drives the current through the power lines for distribution.
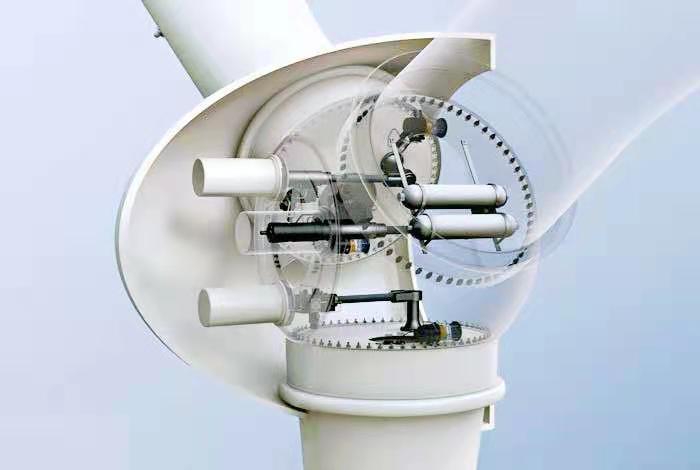
To build a high-efficiency and powerful wind turbine, compared with high-performance ferrite, it is necessary to use a powerful, high-temperature resistant magnet, NdFeB. The high temperature capability is related to its grade. According to market surveys, if the temperature is higher than 160°C, EH series of NdFeB must be used. The ability of each grade is different, especial intrinsic coercivity (Hcj). the better the grade, the higher the Hcj, and of course the higher the price. Wind turbines with tile-shaped magnets as shown in the below picture have better cost performance. Each wind turbine needs a set of magnets. In terms of surface treatment, electroplated zinc, nickel, Or epoxy resin coating. The nickel plating is more cost-effective because it is more resistant to corrosion and high temperature)

Turbine Generator Windmill Magnets:
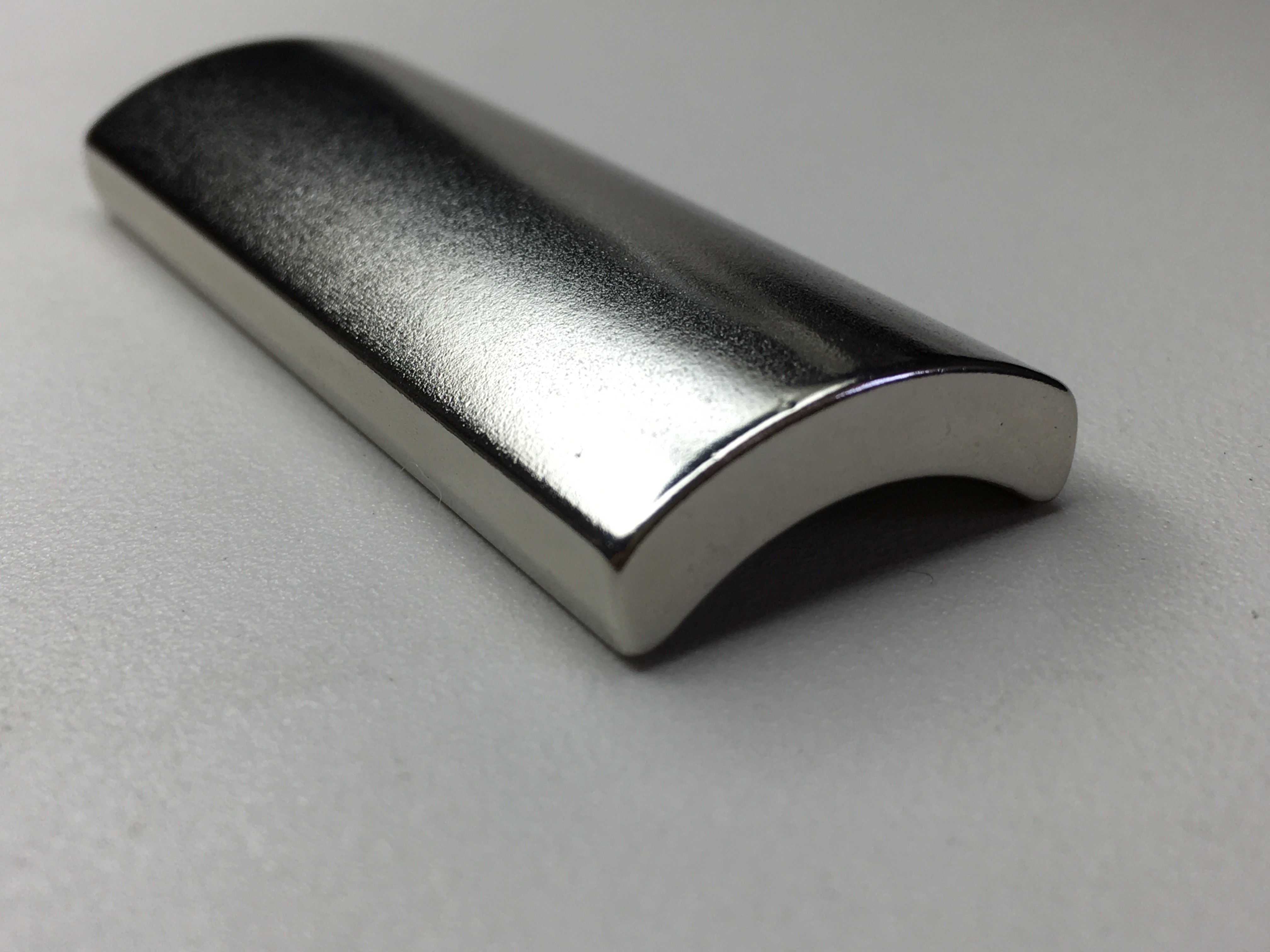
The working environment of the wind turbine is very harsh, it must be able to withstand the test of high temperature, severe cold, sand, humidity and salt spray. Therefore, whether it is a small wind turbine or a megawatt permanent magnet wind turbine, sintered NdFeB permanent magnets are used.

Wind Turbine Generator Windmill Magnets:
It's a permanent magnet alternator, generating 3 phase ac, rectified to dc, and fed to a charge controller.
5. Wind Power-The way electricity is generated
Now that the components of a wind turbine are introduced, the passage will demonstrate how the wind turbine operates and generates electricity. The process of generating electricity is:
Imitating the design of a jet engines, wind turbines overcome a major defect existing in traditional wind turbines. Wind turbines are covered with shields around the blades to guide air through the blades and accelerate them, which increases electricity production. Normally, when the wind passes through the turbine, almost half of the air stays around the blades instead of passing through them all, and therefore, some of the wind power is lost. Traditional wind turbines can only use up to 59.3% of the wind power, a value is called the Betz limit.
Wind turbines are like the intake of jet engines. When air enters, it first encounters a set of fixed blades, called a stator, which can guide the air into a set of rotatable blades, called a rotor. The air pushes the rotor and flows to the other side. At this time, the air moves at a slower speed than it outside the turbine. The shield is made into a suitable shape so that it guides the relatively fast-flowing air outside into the area behind the rotor. The fast-moving air accelerates the slow-moving air, making the area behind the turbine blades low in pressure to draw more air through the blades.
This process is initiated by the turbine blade/rotor. As the wind blows, the aerodynamically-designed blades start to rotate by the wind. When the blades of the wind turbine rotate, the kinetic power of the movement is transferred to the interior of the turbine by a low-speed shaft rotating at a speed of approximately 30 to 60 revolutions per minute (rpm). The low-speed shaft is connected to the gearbox, which is a transmission increases the speed from approximately 30 to 60 rpm, reaching the required rotational speed of the generator, usually between 1,000 and 1,800 rpm. The high-speed shaft transfers the kinetic power from the gearbox to the generator, and then the generator starts to rotate to generate electricity.
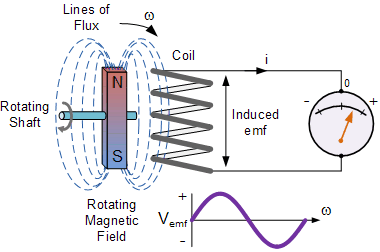
Simple Generator Using Magnetic Induction
Wind Power-Actual output
Because the wind power is unstable, the output of the wind power generator is 13-25V alternating current, which must be rectified by the charger and stored in storage battery, so that the electrical power generated by the wind power generator becomes chemical power. Only after an inverter power supply with a protection circuit converts the chemical power in the battery into standard AC 220V power, can the power be safely used.
Some people believe that the power of wind power is completely determined by the power of the wind turbine, so that people always want to buy a larger wind turbine. This is incorrect. The wind turbine only charges the battery, and it is the battery that stores the electricity. The size of the electric power that people ultimately use is more related to the size of the battery. The amount of power depends more on the air volume rather than the amount of the head power. In the hinterland, small wind turbines work better than large ones. This is because small turbines can be driven by a small amount of wind to generate electricity, and continuous small wind provides more power than a momentary high wind. When there is no wind, people can still use the electricity already produced by the wind. In this way, a 200W wind turbine can be used with a large battery and an inverter to obtain a power output of 500W, 1000W, or even greater.
Wind Power-Application
The use of wind turbines is to continuously convert wind power into standard commercial electricity used by our families. It is a great way to cut cost. The annual electricity consumption of a family only costs 20 yuan for battery fluid. The performance of wind turbines has been greatly improved compared to a few years ago. It was only used in a few remote areas in the past. If a 15W light bulb is directly connected to wind turbines, the light bulb can be damaged because it turned on and off very often. However, due to technological progress and the use of advanced chargers and inverters, wind power generation has become a small high-tech system, and can replace normal mains power under certain conditions.

The Irish offshore wind power plant, with a total capacity of 659 MW, is currently the largest offshore wind power plant in the world.

In Inner Mongolia Huitengxile wind farm, the scale of wind power grid connection reached 20.7 million kilowatts