solutions
Solution/Application
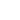
《Magnetic drive pumps》
Magnetic drive pumps, or magnetically coupled pumps, vary from the traditional pumping style, as the motor is coupled to the pump by magnetic means rather than by a direct mechanical shaft. The pump works via a drive magnet, driving the pump rotor, which is magnetically coupled to the primary shaft driven by the motor. They are often used where leakage of the fluid pumped poses a great risk (e.g., aggressive fluid in the chemical or nuclear industry, or electric shock - garden fountains). They have no direct connection between the motor shaft and the impeller, so no gland is needed. There is no risk of leakage, unless the casing is broken.
Since the pump shaft is not supported by bearings outside the pump's housing, support inside the pump is provided by bushings. The pump size of a magnetic drive pumps can go from few Watts power to a giant 1MW.
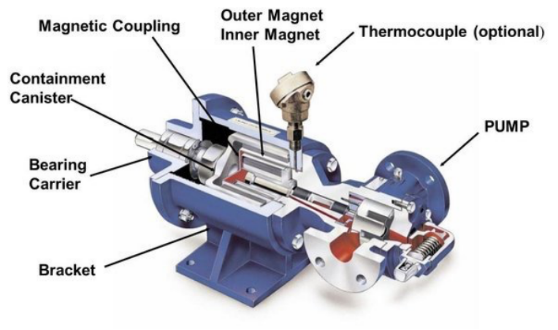
Characteristics (magnetic application):
Generally high Hc (coercive force) NdFeB magnets SH, UH, EH grades or high Hc (coercive force) SmCo magnets are used in magnetic pumps, mostly in block or arc shapes.
Appearance (strict control chip, break, crack, etc), parallelism and perpendicularity are key features for magnetic drive pumps, meanwhile, magnetic property consistency (Br, Hc, Hk) needs to be highlighted in manufacturing, which is critical control point.
Testing:
Magnetic property:
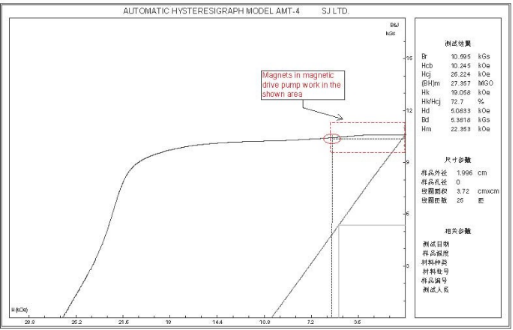
A.Demagnetization curves in room temperature and designated high temperature
Supporting Equipment: Hysteresisgraph
Applicable magnet types: NdFeB, SmCo
B.Irreversible demagnetization by comparing
1.Magnetic flux in room temperature
2.Magnetic flux after magnets are heated in elevated temperature
Supporting Equipment: flux meter, industrial oven
Applicable magnet types: NdFeB, SmCo
Appearance and dimensions
A.Appearance:
1.Salt Spray Test: set in certain humidity, PH based on application
2.Press Cook Test: set in air pressure, temperature and humidity based on application.
3.Plating/Coating thickness; using x-ray-fluorescence to analyze the thickness of surface plating/coating.
Supporting Equipment: SST Cabinet; PCT cabinet; XRF analyzer,
Applicable magnet types: NdFeB, SmCo
B.Dimensions:
1.Geometric tolerances (e.g. parallelism, perpendicularity, etc)
2.Desired size and shape
Supporting Equipment: micrometer, caliper, image measurement tool,
Applicable magnet types: NdFeB, SmCo
《Automobile Magnetic sensors》
Magnetic sensors are used for the detection of positions without contact or wear and tear in control technology. They come into their own where inductive sensors reach their limits.
Magnetic sensors offer small designs with very long sensing ranges. Depending on the orientation of the magnetic field the sensor can be damped from the front or from the side.
Sensor technologies for automotive applications:
position sensor
pressure sensor
temperature sensor
humidity sensor
fluid property sensor
acceleration sensor
……
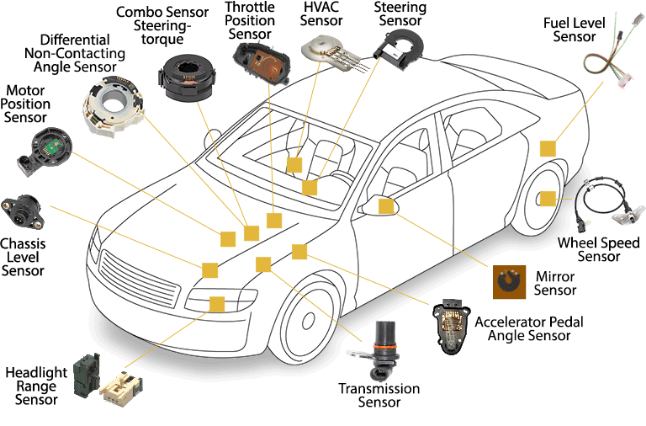
A Hall-effect speed or position sensor integrates a silicon chip with a Hall-effect sensing element and a signal processing circuit. Under the effect of a magnetic field created by a magnet inside the sensor or a magnetic target outside the sensor, the chip generates an electrical signal that can be used to measure speed or position
Speed sensors deliver electrical pulses at each passage of gear teeth or magnetic targets, induced by the alternating north/south magnetic poles.
Position sensors generally deliver a signal that varies continuously with the position of a moving metal or magnetic part.
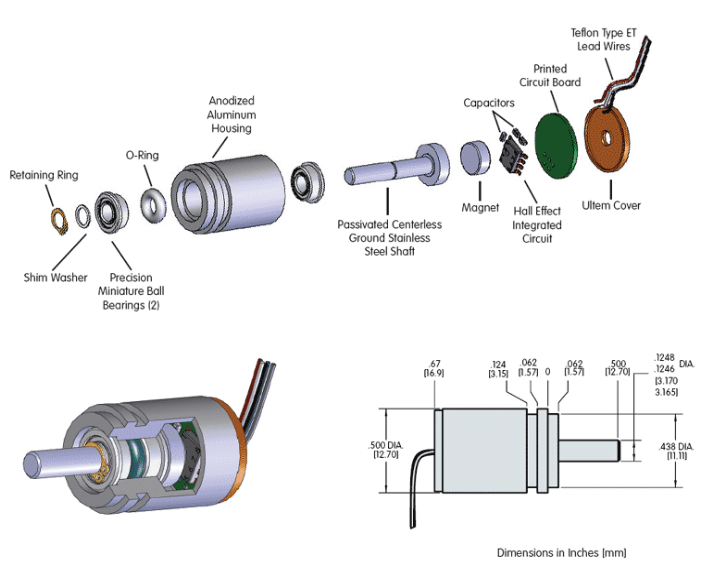
Characteristics (magnetic application):
Of all types and grades of magnets including sintered NdFeB, bonded NdFeB, Sintered SmCo, cast AlNiCo, sintered AlNiCo, hard ferrite, soft ferrite, bonded ferrite, FeCrCo, can be found in various sensors due to its wide applications in all classes of automobiles, cars, vans, buses, trucks, etc.
Generally, the higher class the car, the more sensors and the more magnets applied.
Testing: (cam sensor magnet as an example)
Surface gauss and flux density are 2 major measurement references.
Magnetic property:
Demagnetization curves in room temperature and designated high temperature
Supporting Equipment: Hysteresisgraph
Applicable magnet types: NdFeB magnets, SmCo magnets, hard ferrites
Irreversible demagnetization by comparing
Magnetic flux in room temperature
Magnetic flux after magnets are heated in elevated temperature
Supporting Equipment: flux meter, industrial oven
Applicable magnet types: NdFeB magnets, SmCo magnets, hard ferrite magnets.
Magnetic Deviation Angle
Like the Earth, every magnet is born with declination or variation. It's the angle on the horizontal plane between magnetic north and the designed north (perp to the plane).
Of all the magnet manufacturing processes, molding, pressing, machining (grinding, wire cutting or slicing) could assert great influence to the declination of a magnet.
In sensors, this figure can be of great assistance to design engineers to work out the perfect magnet for their applications.
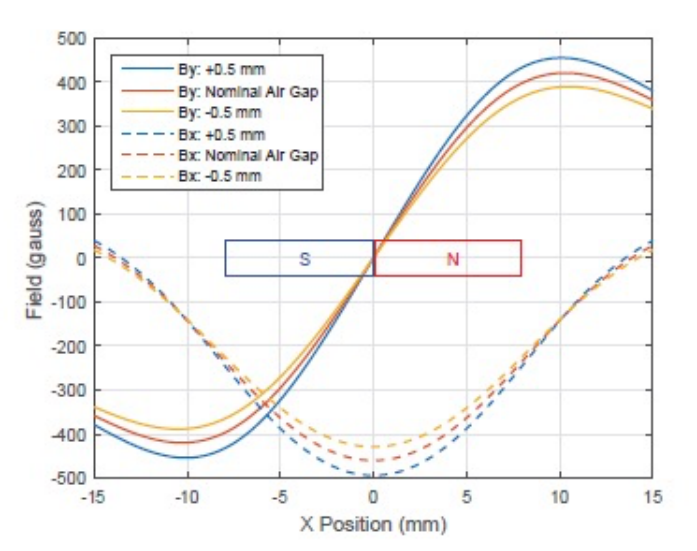
Supporting Equipment: Magnetization Angle Tester
Appearance and dimensions
A.Appearance:
Salt Spray Test: set in certain humidity, PH based on application
Press Cook Test: set in air pressure, temperature and humidity based on application.
Plating/Coating thickness; using x-ray-fluorescence to analyze the thickness of surface plating/coating.
Supporting Equipment: SST Cabinet; PCT cabinet; XRF analyzer,
Applicable magnet types: NdFeB magnets, SmCo magnets, hard ferrite magnets.
B.Dimensions:
1.Geometric tolerances (critical features, e.g. parallelism, perpendicularity, etc)
2.Desired size and shape
Supporting Equipment: micrometer, caliper, image measurement tool, CMM (Coordinate Measurement Machine)
Applicable magnet types: NdFeB, SmCo, hard ferrite magnets.
《Permanent Magnet Servo Motor》
A permanent magnet servomotor is a synchronous motor with feedback for commutation, velocity and position information.
Permanent-magnet motors have some performance advantages over direct-current, excited, synchronous motors, and have become predominant in fractional horsepower applications.
They are smaller, lighter, more efficient and reliable than other singly-fed electric machines.
Originally all large industrial DC motors used wound field or rotor magnets.
Permanent magnets have traditionally only been useful on small motors because it was difficult to find a material capable of retaining a high-strength field. Only recently have advances in materials technology allowed the creation of high-intensity permanent magnets, such as neodymium magnets, allowing the development of compact, high-power motors without the extra real-estate of field coils and excitation means.
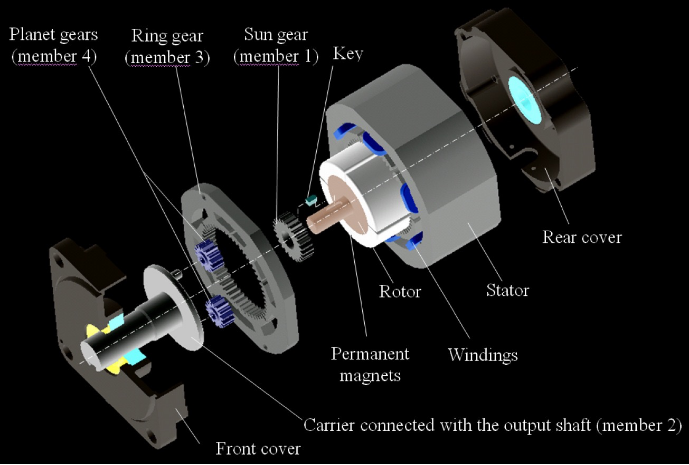
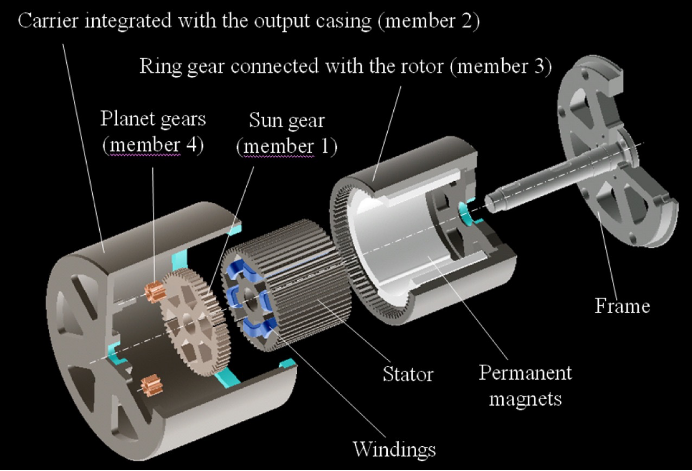
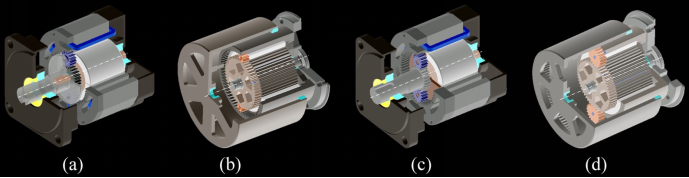
Characteristics (magnetic application):
Permanent magnet materials have been used in electric motors for decades. One important property of permanent magnets is the maximum energy product ((BH)max), which is the multiplication of residual flux density (Br) and coercive force (Hc). In other words, (BH)max represents the maximum energy available per unit volume (kJ/m3). (BH)max is also an indication of magnet force. Furthermore, the larger the (BH)max, the smaller the magnet material needed for the same force. Permeability is another important property of the magnets. It is the slope of the demagnetization curve in the linear region. Small permeability means high flux levels before the magnet is irreversibly demagnetized.
Alnico magnets can be magnetized in any direction by simply heating the magnet and cooling them in a magnetic field to give a preferred magnetic direction.
Traditionally, Alnico magnets were largely used in permanent magnet servo motors. One advantage of Alnico magnets is that they have a high residual flux density (Br). They have excellent temperature stability and strong corrosion resistance level. Their working temperatures can go up to 550 degrees. However, they can be demagnetized easily. In addition, the maximum energy product ((BH)max) of these magnets is not very high.
Ferrite magnets (ceramic magnets), have very high intrinsic coercive force (Hci) and therefore, they are very difficult to demagnetize. They can easily be magnetized in a variety of formats. The raw material is so abundant that it is found in numerous applications. This kind of magnet material has a good resistance to corrosion and can operate at high temperatures up to 300 degrees. These materials are used for permanent magnet server motor where space and cost are not important requirements.
Rare-earth magnets are strong permanent magnets made from the alloys elements such as Neodymium and Samarium. Discovery of these strong magnets have changed the future of permanent magnet motor technology as well as servo motors and the magnetic field can be increased to 1.5T levels.
The first generation rare earth magnets use Samarium and Cobalt (SmCo). One of the biggest advantages of such magnets is that they provide very high maximum energy product ((BH)max) compared to Alnicos and Ferrites. This big improvement in high maximum energy product ((BH)max) is made possible by the high coercive force (Hc). Nonetheless, they are very brittle and both the raw material cost and the production cost are relatively higher than previous 2 types of magnets. Neodymium Iron-Boron (NdFeB) are produced by pressing powders in a magnetic field and their energy products can go up to 440 kJ/m3. This material is stronger than Samarium Cobalt magnets (SmCo) and the cost is relatively lower. However, NdFeB magnets have to be protected against corrosion and exposure to air/liquid and their working temperature is also lower compared to SmCo magnets.
A brief comparison of different magnets used in PM motors is illustrated in the table below. The rare earth magnets are the most common magnet materials used in PM servomotors and the table clearly shows significant benefits of such magnets. NdFeB magnets have higher flux density levels up to 1.5T and higher MEPs but their working temperature is lower (up to 200 oC).
Table 4. Typical permanent magnet material magnetic properties
| Materials | Br [T] | Hc [kA/m] | (BH)max [kJ/m³] | TC [℃] | Tw-max [℃] |
| Alnico | 1.4 | 120 | 96 | 850 | 550 |
| Ferrite | 0.46 | 354 | 42 | 450 | 250 |
| SmCo | 1.2 | 800 | 255 | 820 | 350 |
| NdFeB | 1.5 | 910 | 440 | 380 | 220 |
*All values in the table are maximum figures
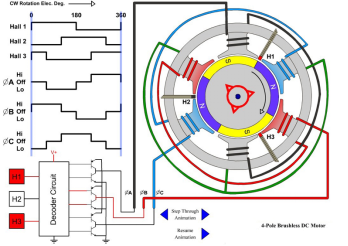
Testing: (permanent magnet servo motor as an example)
Magnetic property:
A.Demagnetization curves in room temperature and designated high temperature
Supporting Equipment: Hysteresisgraph
Applicable magnet types: NdFeB magnets, SmCo magnets, hard ferrites, AlNiCo magnets
B.Irreversible demagnetization by comparing
1.Magnetic flux in room temperature
2.Magnetic flux after magnets are heated in elevated temperature
Important: The consistency of the flux is critical and matters even more after they are mounted on the stator surface. Vector Magnets possesses strict control of flux test for motor magnets so as to ensure the motor would obtain the best possible performance.
Supporting Equipment: flux meter, industrial oven
Applicable magnet types: NdFeB magnets, SmCo magnets, hard ferrite magnets.
Appearance and dimensions
A.Appearance:
Salt Spray Test: set in certain humidity, PH based on application
Press Cook Test: set in air pressure, temperature and humidity based on application.
Plating/Coating thickness; using x-ray-fluorescence to analyze the thickness of surface plating/coating.
Supporting Equipment: Salt Spray Cabinet; Press Cook Test cbinet; XRF analyzer,
Applicable magnet types: NdFeB magnets, SmCo magnets
B.Metal Flaw (crack) Detection
C.Dimensions:
1.Geometric tolerances (critical features, e.g. parallelism, perpendicularity, etc)
2.Desired size and shape
Supporting Equipment: micrometer, caliper, image measurement tool, CMM (Coordinate Measurement Machine)
Applicable magnet types: NdFeB, SmCo, hard ferrite magnets, AlNiCo magnets
《Magnetic separation》
Magnetic separators have applications in a wide array of diverse industries including aggregates, ceramic, chemical, coal, food, glass, light industries, metalworking, minerals, processing, packaging, pharmaceutical, plastics & rubber and recycling.
Permanent and electromagnetic magnetic separators are available in a variety of designs, including, magnetic plates, grates, drawers, drums, humps, pulleys, spouts, belts etc.
Whether your product is gravity fed through pipes and chutes, loosely transported on conveyors and/or pumped through pipelines, Vector has the magnetic separation solution. Magnetic Separators are designed specially to deal with contaminants like nails, rust, scale, bolts, welding rods, etc
Permanent Magnetic Separators work with no electric power. They can last a lifetime with very little loss of field strength, approximately 1/10 of 1% per year. Permanent Magnetic Separators using ceramic or Rare Earth material for increased strength and extended magnet life.
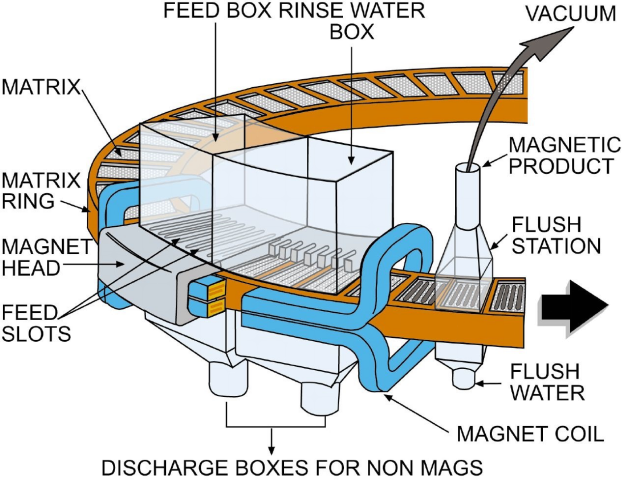
Applied Magnetic Materials:
Type:
1.Hard ferrite magnets
2.Sintered NdFeB magnets
Testing:
Magnetic property:
A.Demagnetization curves in room temperature
B.Surface gauss and flux density
Supporting Equipment: Hysteresisgraph, gauss meter, flux meter
Appearance and dimensions
A.Visual Inspection on chips, burrs, cracks or any other breaks
B.Desired size and shape
Supporting Equipment: micrometer, plastic caliper*
Packing:
To protect the operators from getting injured by these magnets in big size and strong in property, thick wood or plastic spacer is a necessity for loading and unloading.
plastic caliper*,
magnetic separator magnets are generally very strong and big, caliper with ferrous element could be massively damaged and the operator could get injured very easily. Thus, non-ferrous measurement instrument is suggested.
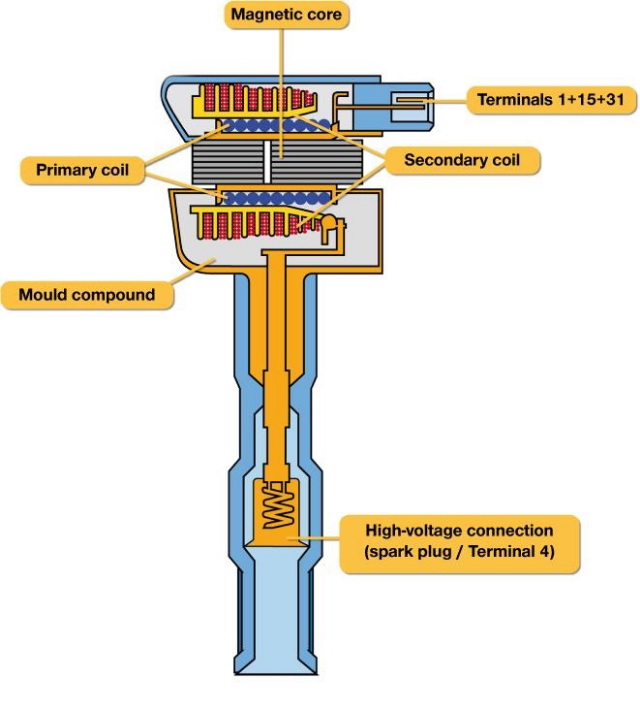
《Ignition Coil》
An ignition coil (also called a spark coil) is an induction coil in an automobile's ignition system which transforms the battery's low voltage to the thousands of volts needed to create an electric spark in the spark plugs to ignite the fuel.
An ignition coil consists of a laminated iron core surrounded by two coils of copper wire. Unlike a power transformer, an ignition coil has an open magnetic circuit - the iron core does not form a closed loop around the windings. The energy that is stored in the magnetic field of the core is the energy that is transferred to the spark plug.
Current technology coils are of several basic types, say, pencil coils. Pencil coils are typically an inch in diameter and up to four inches long. These coils are designed to fit in between the cams of DOHC (double overhead camshaft) and SOHC (single overhead camshaft) engines. The normal practice for pencil coils is to include the switching electronics needed to control the coil, in a small pocket near the outer end of the coil package.
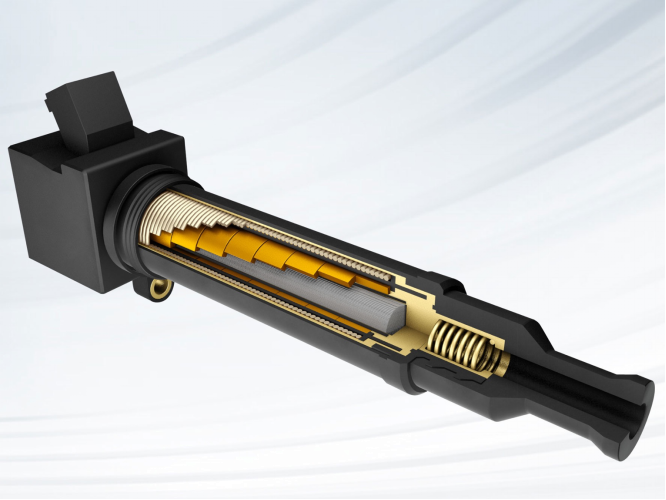

Characteristics (magnetic application):
In a spark plug ignition assembly for a spark plug, an ignition coil assembly has a steel laminated core, said core having a first core portion and a second core portion, and a primary winding around the first core portion and a secondary winding around the primary winding. A spark plug connecting member is provided for connecting the coil assembly to the spark plug. At least one of the first and second core portions has a slot therein with a magnet located in the slot.
Applied Magnetic Materials:
Type:
1.Elevated Temperature NdFeB including UH, EH and AH grades.
2.High Hcj (intrinsic coercive force) SmCo, like SmCo 26H, SmCo 28H, SmCo 30H. Generally, Hcj (intrinsic coercive force) of these magnets is greater than 18 kOe.
Dimensions:
1.Disc: diameter ranges from 5mm to 20mm, thickness from 0.7mm to 1.8mm
2.Rectangular: length/width ranges from 8mm to 20mm, thickness from 0.7mm to 1.8mm
Testing:
Magnetic property:
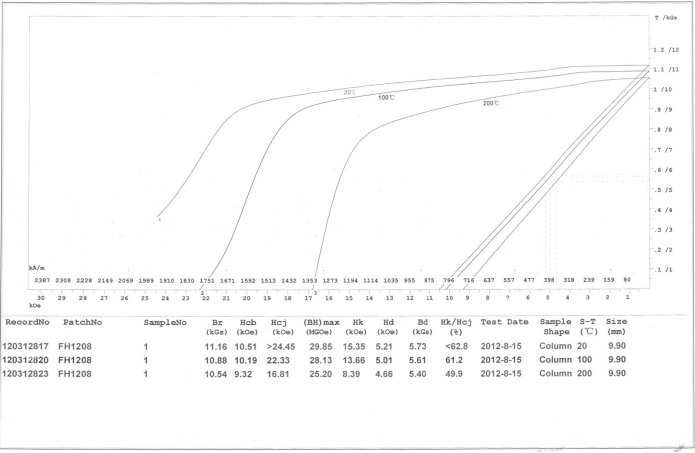
A.Demagnetization curves in room temperature and designated high temperature
B.Hk: demagnetization field that reduces the remanence (Br) by certain amount in accordance to requirement
Supporting Equipment: Hysteresisgraph
B.Irreversible demagnetization by comparing
1.Magnetic flux in room temperature
2.Magnetic flux after magnets are heated in elevated temperature
Supporting Equipment: flux meter, industrial oven
Important: The consistency of the flux is critical and matters even more. Vector Magnets possesses strict control of flux test for ignition coil magnets so as to ensure the ignition coil would obtain the best possible performance.
Appearance and dimensions
A.Appearance:
Salt Spray Test: set in certain humidity, PH based on application
Plating/Coating thickness; using x-ray-fluorescence to analyze the thickness of surface plating/coating.
Supporting Equipment: Salt Spray Test Cabinet; XRF analyzer,
B.Dimensions:
1.Geometric tolerances (e.g. parallelism, perpendicularity, flatness, etc)
2.Desired size and shape